Pokročilé technológie /
Nickel coating of carbon fibres to increase electric conductivity in polymer matrix composites.
 Copper coated of Torayca T-300 carbon fibres
Copper coated of Torayca T-300 carbon fibres
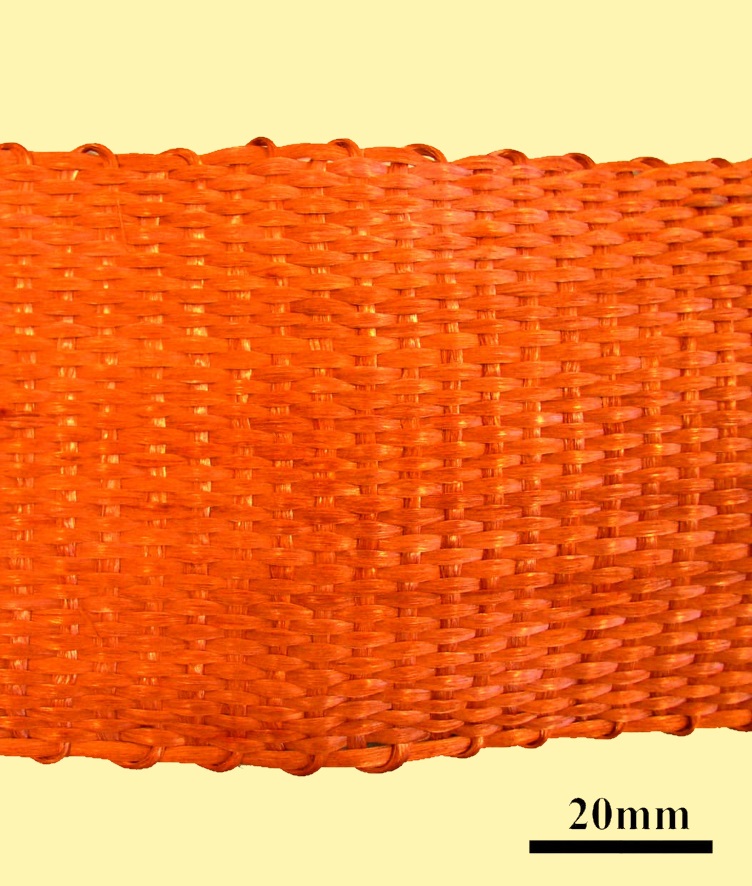 Fabric made from copper coated carbon fibre tow
Fabric made from copper coated carbon fibre tow
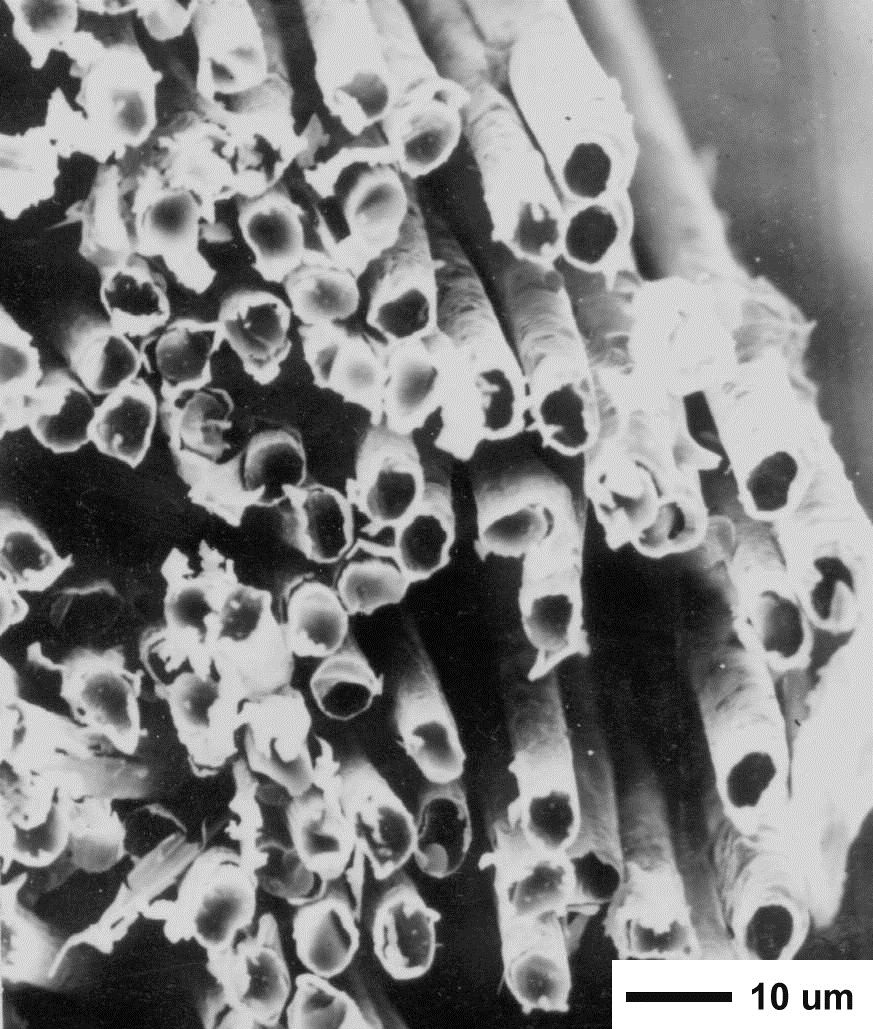
 Cross sectional view of Ni coated carbon fibres
Cross sectional view of Ni coated carbon fibres
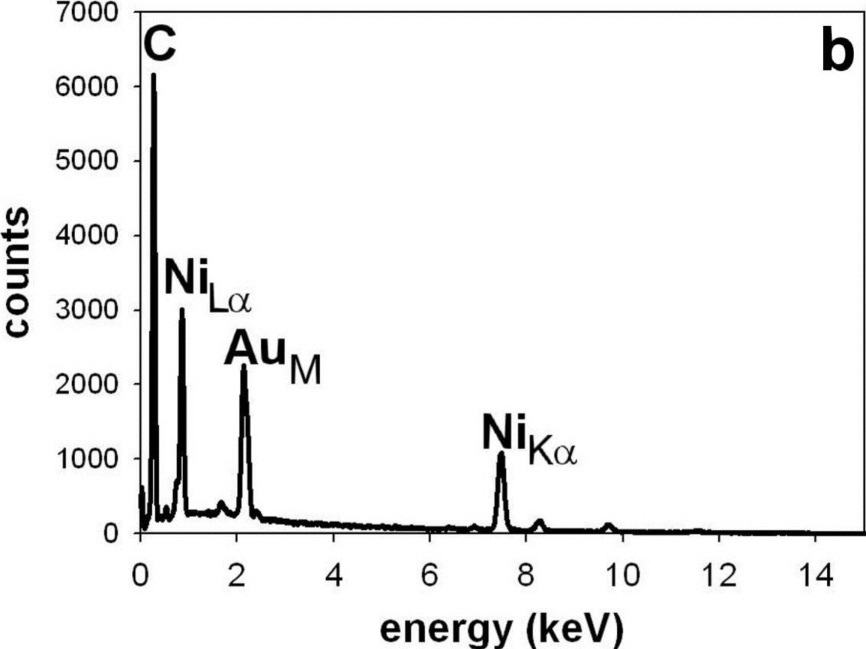 EDS spectrum acquired from Ni coating (point +)
EDS spectrum acquired from Ni coating (point +)
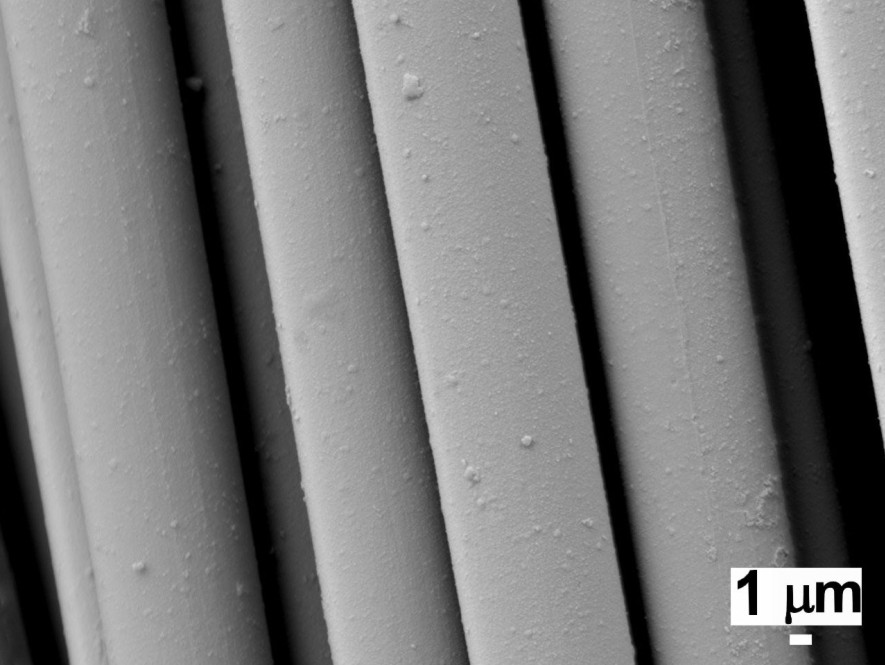 Ni coated carbon fibre tow
Ni coated carbon fibre tow
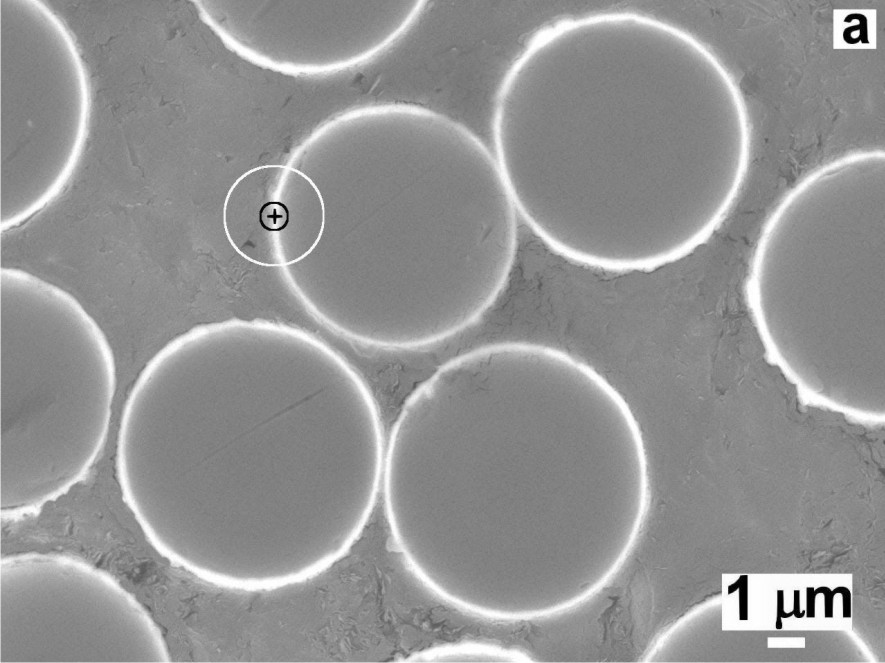
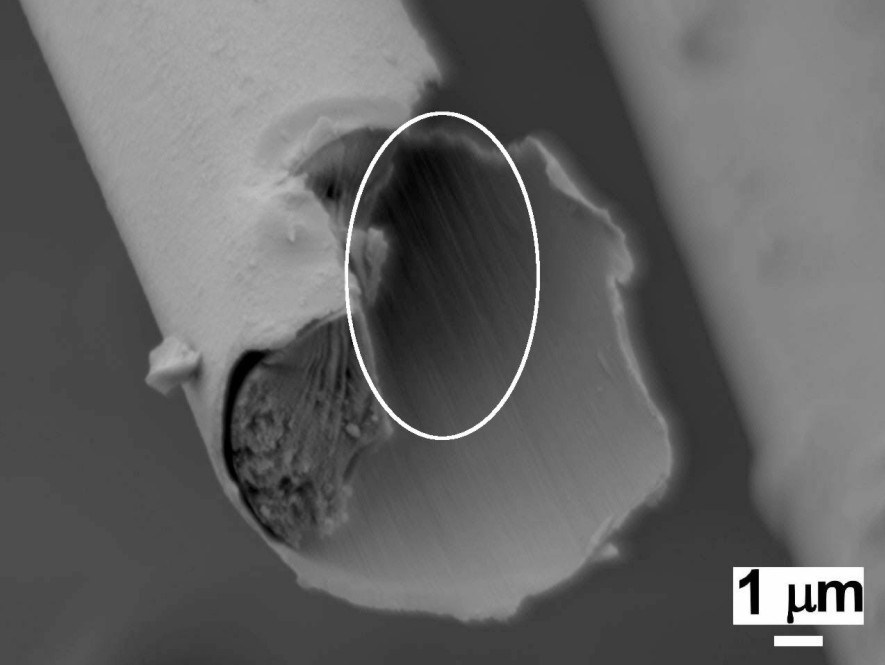 Ni coating imprinting the C fibre surface morphology
Ni coating imprinting the C fibre surface morphology
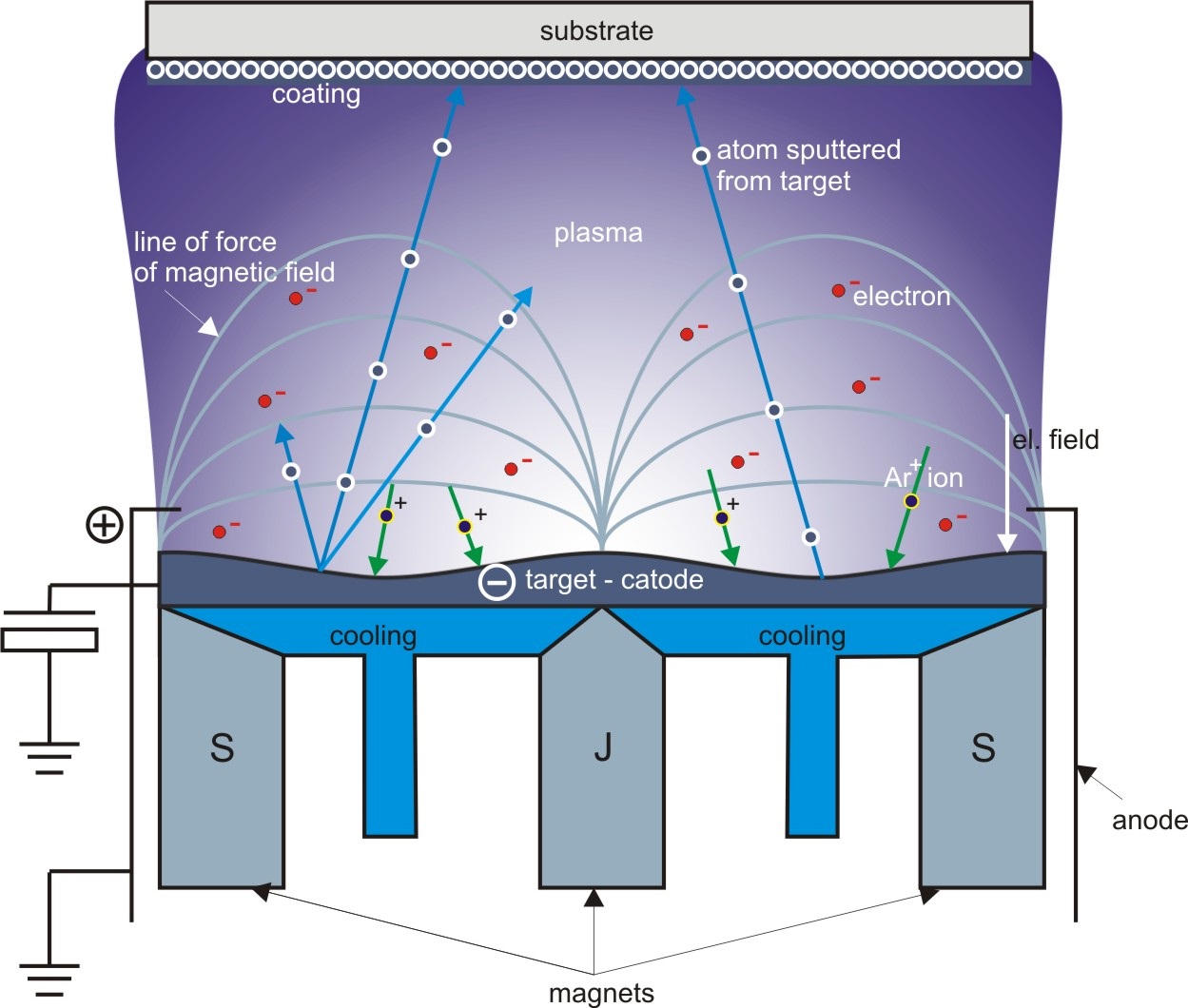 Principle of magnetron sputtering
Principle of magnetron sputtering
Techniky povlakovania
Fibre coating
General description
Diffusion bonding of coated multifilament fibre tows is used for the preparation of metal matrix composites (MMCs). Some coated layers prevent reaction between fibres and matrix or increase the surface wettability of fibres by molten metal.Principle of operation
Metal coatings on continuous multifilament carbon fibre tows can be obtained by various technologies, such as chemical vapour deposition (CVD) process, physical vapour deposition (PVD) process, autocatalytic (electroless) plating process, electrolytic (galvanic), etc. All methods related to metals deposition on strand of fibres have common problem – i.e. how to spread effectively the tow at the beginning of the deposition process.Typical applications
Preparation of copper matrix/carbon fibre composite.Nickel coating of carbon fibres to increase electric conductivity in polymer matrix composites.
 Copper coated of Torayca T-300 carbon fibres
Copper coated of Torayca T-300 carbon fibres Fabric made from copper coated carbon fibre tow
Fabric made from copper coated carbon fibre tow Cross sectional view of Ni coated carbon fibres
Cross sectional view of Ni coated carbon fibres EDS spectrum acquired from Ni coating (point +)
EDS spectrum acquired from Ni coating (point +) Ni coated carbon fibre tow
Ni coated carbon fibre tow Ni coating imprinting the C fibre surface morphology
Ni coating imprinting the C fibre surface morphologyEquipment
- Lab-scale facility with several steps – desizing, electroless metal coating, galvanic metal coating, winding
Plasma coating
Physical vapor deposition
General description
Physical vapor deposition presents a group of deposition techniques (evaporation, magnetron sputtering, and pulsed laser deposition) for preparation of thin films and coatings with thickness in the range from several nanometers to micrometers.Principle of operation
Magnetron sputtering represents one of the mostly used PVD deposition techniques. Magnetron sputtering is a plasma coating process whereby sputtering material is ejected due to bombardment of ions to the target surface. The vacuum chamber of the PVD coating machine is filled with an inert gas, such as argon or reactive gas, such as nitrogen or oxygen. By applying a high voltage, a glow discharge is created, resulting in acceleration of ions to the target surface. The argon-ions will eject sputtering materials from the target surface (sputtering), resulting in a sputtered coating layer on the products in front of the target.Typical applications
- hard, wear resistant coatings
- low-friction coatings
- corrosion resistant coatings
- decorative coatings
- superconducting coatings
- coatings with specific optical, or electrical properties
- protective coatings for high-temperature applications
 Principle of magnetron sputtering
Principle of magnetron sputteringEquipment
- Lab-scale facility with two-steps vacuum pumping system (rotary and turbomolecular pump), mass flow controllers, two gas inlets, 4” unbalanced magnetron, biased and heated substrate holder, DC power supply for magnetron and for bias.